The larvae show a wide array of adaptations to the pelagic environment, including modifications in functional morphology, anatomy, the molting cycle, nutrition, growth, chemical compositionDownload scientific diagram 1 Larval forms in crustaceans Comparison with adults (examples) (AC) Cirripedia Tetraclita squamosal and T formosana (A) Nauplius (B) Cypris Sessile What are the larval forms of crustacea?

Crustacean Larva Wikipedia
Larval forms of crustacea ppt
Larval forms of crustacea ppt-LARVAL FORMS OF CRUSTACEA Crustaceans are Arthropods whose body is covered with chitinous exoskeleton for protection But the same exoskeleton does not allow body growth and hence must be shed in order to allow growth The larval stages feed and grow in order to become adults and must undergo moulting or ecdysis to growThe appendages are very elongate and slender;



Crustaceans Chapter Ppt Video Online Download
Crustaceans may pass through a number of larval and immature stages between hatching from their eggs and reaching their adult form Each of the stages is separated by a moult, in which the hard exoskeleton is shed to allow the animal to grow The larvae of crustaceans often bear little resemblance to the adult, and there are still cases where it is not known what larvae will growLarval forms of invertebrates ppt lasercosmeticapl {{ Keyword }} The larval development of three crabs of the Varunidae family, (Hemigrapsus sanguineus, H penicillatus, and H longitarsis), widely spread in Russian waters of the Sea of Japan, were studied under laboratory conditions At a temperature of –22°C and a salinity of 32‰ about 30% of larvae a complete developmental cycle, including five zoeal stages and megalopa, took
Crustaceans are a group of organisms belong to the Class Crustacea of Phylum Arthropoda Most of them undergo indirect development and possess one or more la Larval forms in Arthropoda 1 Nauplius larva • Discovered by Muller in 18th century, the Nauplius larva is the first fundamental stage in all crustaceans that sometimes hatches from the egg and sometimes passes inside the egg • Body is oval in shape and unsegmented with a large cephalothorax and rudimentary abdomenThe following points highlight the fifteen different types of Crustacean larva The types are 1 Nauplius Larva 2 Metanauplius Larva 3 Cypris Larva 4 Protozoea Larva 5 Zoea Larva 6 Mysis Larva 7 Metazoea Larva 8 Megalopa Larva 9 Kentrogen Larva 10 Epicaridian Larva 11 Cryptoniscus Larva 12 Erichthoidina Larva 13 Erichthus Larva 14
SESSILE CRUSTACEANS Barnacles are a group of crustaceans that are sessile as adults Freeswimming larvae attach themselves to a rock, post, or some other submerged object, where they remain Hard plates that can open and close protect the barnacle's body When feeding, barnacles extend their jointed feeding appendages (legs) through the open plates Their feathery legs stirI n most crustacea, development is accompanied by little or more metamorphosis and the various stages of development are known as larvae They are nauplius, metanauplius, cypris, kentrogen, protozoea, zoea, metazoea, calyptosis, erichthus, alima, megalopa, glaucothoea, mysis and phyllosomaIn this article we will discuss about the nauplius, zoea and megalopa larva of crustaceans with the help of suitable diagrams Nauplius Larva of Crustaceans Fig 147 NAUPLIUS LARVA WM 1 It is the slide of Nauplius larva, which is the earliest free swimming stage in



Effects Of Reduced Salinity Caused By Reclamation On Population And Physiological Characteristics Of The Sesarmid Crab Chiromantes Dehaani Scientific Reports



Larval Crab High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
Ppt_debolina View presentation slides online Read free for 30 daysHome > 新闻动态 > larval forms of cestodes ppt larval forms of cestodes ppt Posted 16 June 21; Hosts of Crustacean Parasites In biology, a host is an organism that harbours a parasite, typically providing nourishment and shelter Parasitic Crustaceans use representative from many metazoan phyla Ex Fish, Jellyfish, Ascidians, Corals etc Crustaceans itself also serves as host to other parasitic crustaceans Ex Crab, Shrimps etc 10



2




Crustaceans Chapter Ppt Video Online Download
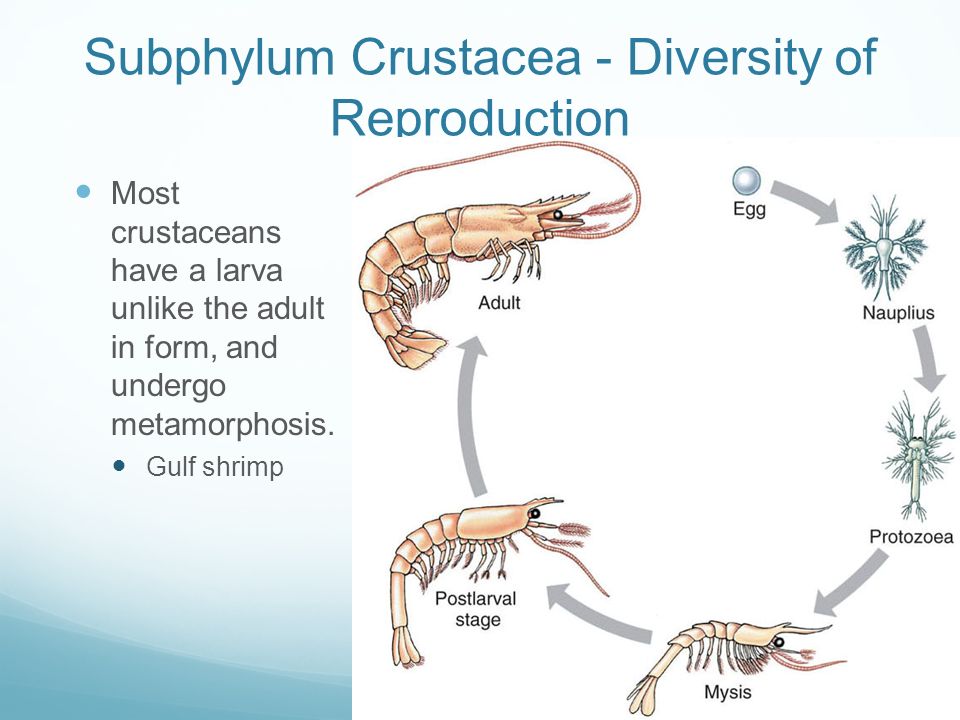
CRUSTACEANS Arthropods in the water! The fundamental body structures of shrimpshaped and crabshaped decapod crustaceans were compared and discussed based on larval morphology Penaeus japonicus was selected as a representative shrimpshaped form, since it has ancestral characteristics and eight pairs of natatory thoracic appendagesLarval forms in crustaceans 1 LARVAL FORMS OF CRUSTEANS 2 NAUPLIUS Nauplius is the first and the fundamental larva of most of crustaceans It is minite,free 3 Antennular appendages are uniramous, and the others are biramous Anus is located at the posterior tip Nauplius 4




The Oldest Peracarid Crustacean Reveals A Late Devonian Freshwater Colonization By Isopod Relatives Biology Letters




Crustaceans Lat Crustacea One Of The Classes Of Arthropods Prezentaciya Onlajn
Morphology of the Zoeae Larvae of Brachyura (Crustacea, Decapoda) vol 15, pp 1131, 1972 242 Sergio CházaroOlvera et al 31 HSkip to content Menu RSS2 General features Almost all crustaceans have an exoskeleton hardened with calcium salts that covers most of the animal as a protective shell carapace All have 2 pair of antennae;



Larvial Forms Of Echinoderms With Diagram




Crustacean Development I Life Cycle Ppt Video Online Download
Distally they possess a subchelate claw for grasping jellyfish or combjellies Phyllosoma larvae can reach astonishing sizes of up to 150 mmCrustaceans may pass through a number of larval and immature stages between hatching from their eggs and reaching their adult form Each of the stages is separated by a moult, in which the hard exoskeleton is shed to allow the animal to grow The larvae of crustaceans often bear little resemblance to the adult, and there are still cases where it is not known what larvae will growHii Guys Welcome to our channelThis is Yashaswi Vyas Mam And She is providing you cell biology bsc 1st year // 11th class SBSE & RBSE //RRB NTPC // GROUP D




Ppt Crustacean Development I Life Cycle Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Basic Taxonomy Of Marine Organisms Springerlink
The main subject of this book is the postulated transfer of embryonic and larval forms from one phylogenetic line to another, and I start with the decapod crustaceans This is a group that contains very few examples that can be attributed to this phenomenon, but the case of the Dromioidea is particularly important3 Body morphology 4 Body anatomy 5 Nauplius Almost allof crustaceans have distinctive larval form nauplius These larval stages are different from the adult in form and structure The larval stages achieve adulthood through the process of metamorphosis The following is the detailed explanation of each of the larval forms of crustaceans Nauplius larva It is the first larvae hatched from egg in most of the crustaceans It is free swimming larvae




Food And Feeding Habits Of Larvae Of Finfishes Ppt



1
Crustaceans are a very diverse group of invertebrate animals which includes active animals such as the crabs, lobsters, shrimp, krill, copepods, amphipods, and more sessile creatures like barnacles Arthropoda is the largest phylum of Animal Kingdom It includes about 11,340,000 species in all habitatsAll Arthropods have 1 Exoskeleton 2 Jointed Legs Lobsters Shrimp Crabs Barnacles EXAMPLES OF CRUSTACEANS CRUSTACEAN INFO – A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as a Flash slide show) on PowerShowcom id 6f6ca5NDMxNLARVAL FORMS OF CRUSTACEA Crustaceans are Arthropods whose body is covered with chitinous exoskeleton for protection But the same exoskeleton does not allow body growth and hence must be shed in order to allow growth The larval stages feed and grow in order to become adults and must undergo moulting or ecdysis to grow



2




Crustaceans Chapter Ppt Video Online Download
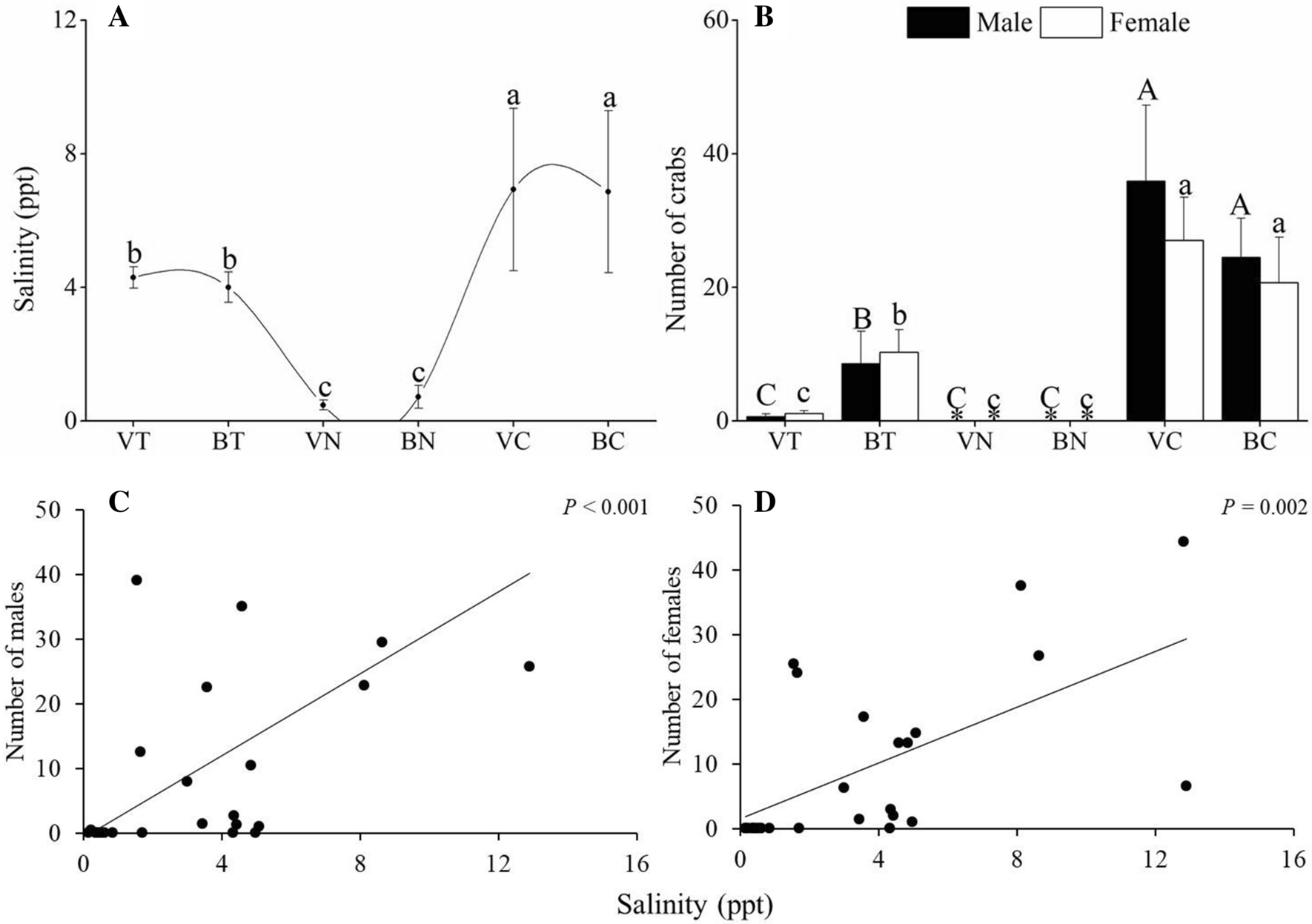
Since that larval stages of crustaceans species in estuaries, undergo development under this range of environmental conditions, Paula et al (Reference Paula, Mendes, Paci, McLaughlin, Gherardi and Emmerson 01) studied the temperature and salinity effects on the larval development of Upogebia africana Ortmann, Reference Ortmann and Semon 14, in relation toLarval Form # 7 Megalopa Larva Megalopa larva has a large unsegmented cephalothorax with all 13 pairs of appendages like those of a crab, abdomen is straight and in line with cephalothorax, it is like the abdomen of prawn with 6 pairs of well formed pleopods, In crabs the nauplius is passed in the egg, it hatches as a zoaea which by moulting forms the megalopa stage, the megalopa byTitle CRUSTACEANS 1 CRUSTACEANS PETRA BÍROVÁ;




Ch 33 Ppt



Frontiers Anterior Hox Genes And The Process Of Cephalization Cell And Developmental Biology
Development that release cypris larvae into the external environment 8, 30 Rhizocephalan larvae are heterosexual In species with kentrogonid type of development, female cypris larvae settle on a new host and molt into a highly specialized stage, the kentrogon, which injects with a cuticular stylet through the integument the next stageLarvae were hatched on 17th March, 1996, at room temperature of 26oC and water temperature 23oC in filtered seawater of a salinity of 3537 ppt and pH 79 81 All the larval stages of Saron larval forms of crustaceans Here you can post pictures and videos to show others 8 posts • Page 1 of 1 Message Author Sabatini Posts 371 Joined Tue 309 am larval forms of crustaceans #1 Post by Sabatini » Tue 858 pm Hi




Hickman Chapter 13 Final Ppt




Phylum Arthropoda Larval Forms In Crustaceae Study Score
1 CRUSTACEA 2 • Phylum Arthopoda • Subphylum Crustacea • 30,000 species • Mostly marine 3 Examples of Crustaceans Crabs 4 Examples of Crustaceans Shrimp 5 Examples of Crustaceans Lobster 6 Examples of Crustaceans Barnacles 7 Examples of Crustaceans Copepods – 70% of all Crustaceans 8Larval form = nauplius larva Animals Arthropoda Crustacea;These larvae are among the most aberrantappearing larval forms of all crustaceans The body is leaflike (name!), flat and translucent;



Larval Crab High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




1 Objectives 1 To Examine The Anatomy And
Crustaceans larval forms Larval forms of crustaceans pdf Larval forms of crustaceans ppt The MONODON crustás of larva and adults of the larva and adults, the crustás of Penaeus Monodon can go through a series of larval and immature stages between the hatching of their eggs and reach their adult formPabst T, Richter S (04) The larval development of an Australian limnadiid clam shrimp (Crustacea, Branchiopoda, Spinicaudata), and a comparison with other Limnadiidae Zool Anz –115 Google Scholar Pai PG (1958) On postembryonic stages of phyllopod crustaceans, Triops ( Apus ), Streptocephalus and EstheriaNow, you do not need to roam here and there for larval forms of crustaceans ppt links Checkout this page to get all sort of ppt page links associated with larval forms of crustaceans ppt PowerPoint Presentation Characteristic crustacean larval stage nauplius




Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum Crustacea Ppt Video Online Download




A Phylogenomic Framework Evolutionary Timeline And Genomic Resources For Comparative Studies Of Decapod Crustaceans Proceedings Of The Royal Society B Biological Sciences
Crustaceans may pass through a number of larval and immature stages between hatching from their eggs and reaching their adult form Each of the stages is separated by a moult, in which the hard exoskeleton is shed to allow the animal to grow The larvae of crustaceans often bear little resemblance to the adult, and there are still cases where it is not known what larvae will growThe present report is based on the study of sample collected from Ghora Bari (Makri Creek) on for the purpose of nonpenaeid shrimps exploitation The sample, besides having shrimps have fishes belonging to several species and isopodFirst report of larval forms of paragnathia sp(crustacea isopoda gnathidae) from pakistani waters (makri creek)




Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum Crustacea Ppt Video Online Download




Larval Development And Settlement Of A Whale Barnacle Biology Letters
Larval forms of crustaceans 1 Larval forms of crustaceans By Samina HUSAIN 2 SYNOPSIS Introduction Larval forms of CRUSTACEA Nauplius larva included in ORDER DECAPODA Metanauplius larva included in ORDER NOSTOSTRACA Cyris larva included in ORDERRHIZOCEPHALA Protozoaea larva included in ORDER EUPHAUSIACEA Zoaea larva Crustacean larvae are usually recognised as small organisms, below one millimeter body size However, in different crustacean groups such as Stomatopoda, Polychelida, or Achelata, also very large larvae occur with sizes of mm and beyond Also from few meiuran species ("shorttailed" crustaceans, including crabs, hermit crabs, or squat lobsters), rather largeFIRST REPORT OF LARVAL FORMS OF PARAGNATHIA SP (CRUSTACEA ISOPODA GNATHIDAE) FROM PAKISTANI WATERS (MAKRI CREEK) salinity 42 ppt and pH 87 The larvae inspected all were zuphea and praniza stage The larvae were preserved in 5% formalin, dissected with a tungsten needle under a binocular microscope Kyowa ( X magnification)




Phylum Arthropoda Larval Forms In Crustaceae Study Score




The Role Of Feeding Morphology And Competition In Governing The Diet Breadth Of Sympatric Stomatopod Crustaceans Biology Letters
For many people, the term crustacean conjures up images of cooked lobsters, shrimp and crabs While these particular animals embody many of the usual crustacean characteristics, they represent only a tiny fraction of this remarkable assemblage of animals (Figure 1) Crustaceans belong to the phylum Arthropoda, which is usually subdivided into four major Exotic larval morphologies abound in the Decapoda, for instance phyllosoma larvae and a plethora of nominal taxa of larval forms not yet linked toClass Crustacea Subclass Copepoda Order Eucopepoda Suborder Cyclopoida Immature copepods Description Plate 0a Nauplius larvae of copepod Plate 0b – A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as a Flash slide show) on PowerShowcom id 6f36a7YTA5M




The Molting A And Survival B Rate Of Larvae Exposed To Artificial Download Scientific Diagram




Phylum Arthropoda Larval Forms In Crustaceae Study Score
Ziser Lecture Notes, , 1611 2 pr antennae 3 prs appendages 1 pr mandibles all function as swimming appendages at this stage from the nauplius stage often develop other distinctive larval forms for different groups of crustaceans eg zoea larva – some crabs




Ppt




Percent Survival Se Of Each Stage Of Scylla Serrata Larvae And Download Scientific Diagram




Morphology And Molecular Phylogeny Of Ornamental Freshwater Prawns Of The Genus Macrobrachium Decapoda Caridea Palaemonidae From China With The Description Of A New Species In Crustaceana Volume 94 Issue 10 21
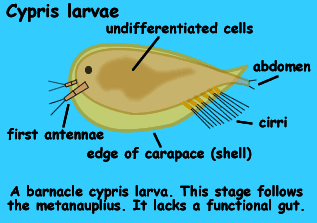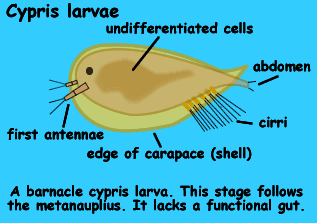



User Alka Yadav Assigment On Crustacean Larva Wikieducator



The Implications Of Temperature Mediated Plasticity In Larval Instar Number For Development Within A Marine Invertebrate The Shrimp Palaemonetes Varians



2




Crustaceans Insects Of The Sea Ppt Download




Phylum Arthropoda Larval Forms In Crustaceae Study Score
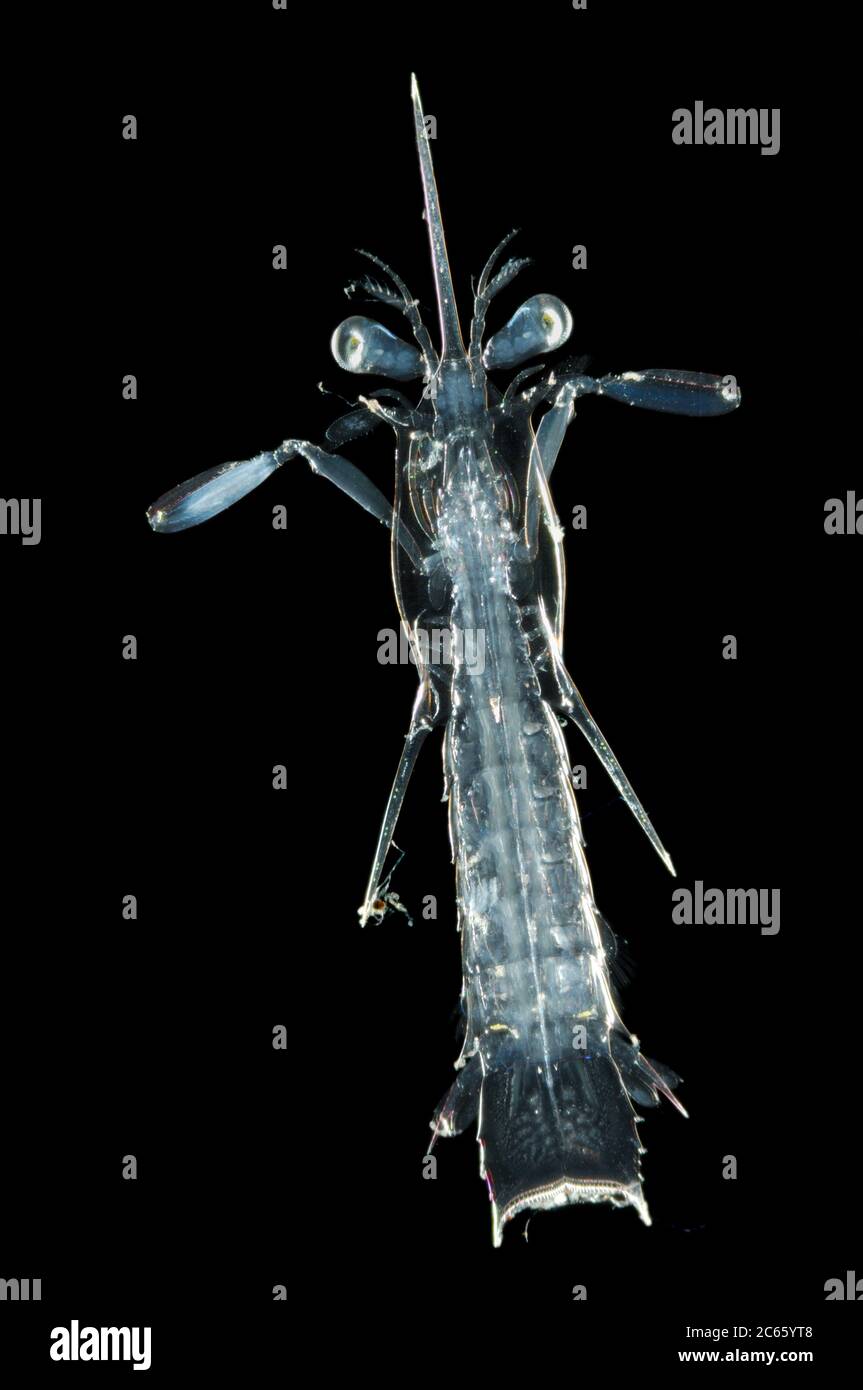



5 Larval Stage High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




The Origin Of Barnacles Thecostraca Cirripedia In Crustaceana Volume 87 Issue 6 14




Larval Forms Of Crustaceans




Arthropods Part 2 Ppt Classification Of Arthropods 5 Subphyla U22 Phylum Arthropoda U13 Subphylum Pycnogonida U13 Subphylum Crustacea U13 Subphylum Course Hero




Crustacean Larva Wikipedia




Crustacean Larva Wikipedia




Crustaceans Preservation Ppt Powerpoint




Larval Crab High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



1




The Origin Of Barnacles Thecostraca Cirripedia In Crustaceana Volume 87 Issue 6 14




Ppt Crustaceans The Insect Of The Sea Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




References In Infections Related To The Ingestion Of Seafood Part Ii Parasitic Infections And Food Safety The Lancet Infectious Diseases




Phylum Arthropoda Larval Forms In Crustaceae Study Score




Larval Forms In Crustaceans




Crustacean Larva Wikipedia



Longdom Org




Crustacean Larva An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Modeled Buoyancy Of Eggs And Larvae Of The Deep Sea Shrimp Aristeus Antennatus Crustacea Decapoda In The Northwestern Mediterranean Sea



1




Larval Forms Of Crustaceans




Abbreviation Of Larval Development And Extension Of Brood Care As Key Features Of The Evolution Of Freshwater Decapoda Vogt 13 Biological Reviews Wiley Online Library



2




Crustaceans Chapter Ppt Video Online Download




Course Outline




Effect Of Methyl Farnesoate And Farnesoic Acid During 5th Zoea And Megalopa Metamorphosis In The Mud Crab Scylla Paramamosain Estampador 1950 Decapoda Brachyura Portunidae In Crustaceana Volume 94 Issue 7 21




Complete Larval Development Of Thenus Unimaculatus Burton Davie 07 Decapoda Scyllaridae In Crustaceana Volume 87 Issue 5 14




The Natural History Of The Crustacea Volume 8 Evolution And Biogeography Of The Crustacea Nhbs Academic Professional Books
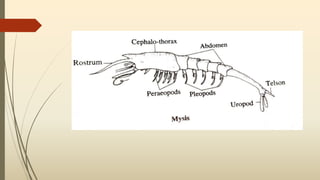



Larval Forms In Crustaceans




Percent Survival Se Of Each Stage Of Scylla Serrata Larvae And Download Scientific Diagram




Development Of Embryos And Larvae Of Portunus Trituberculatus Decapoda Brachyura In Off Season Breeding Mode In Crustaceana Volume 94 Issue 6 21




Phylum Arthropoda Larval Forms In Crustaceae Study Score
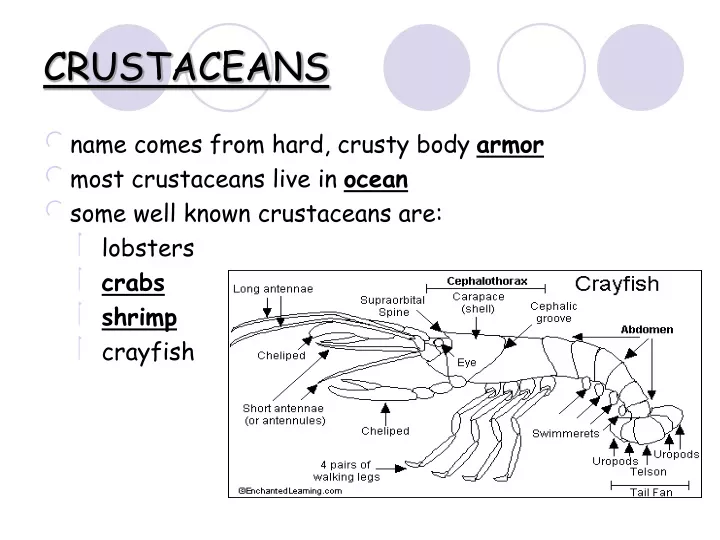



Ppt Crustaceans Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



2




Fao Penaeus Monodon Fabricius




Ppt Crustacean Development I Life Cycle Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Three Dimensionally Preserved Minute Larva Of A Great Appendage Arthropod From The Early Cambrian Chengjiang Biota Pnas




Abbreviation Of Larval Development And Extension Of Brood Care As Key Features Of The Evolution Of Freshwater Decapoda Vogt 13 Biological Reviews Wiley Online Library
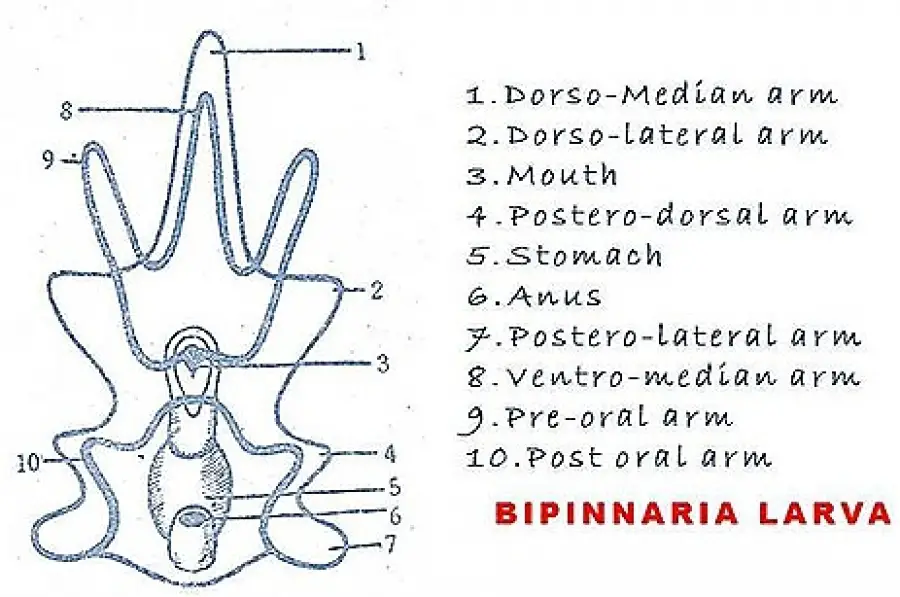



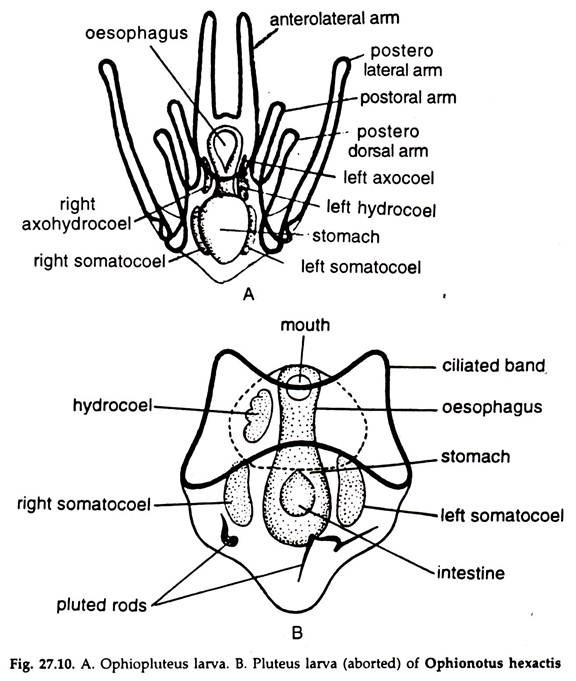
Forms Of Echinodermata Larva




Crustaceans Powerpoint In 22 Crustaceans Pill Bug Powerpoint



Modeled Buoyancy Of Eggs And Larvae Of The Deep Sea Shrimp Aristeus Antennatus Crustacea Decapoda In The Northwestern Mediterranean Sea




Part 1 Larval Forms Of Crustaceans Introduction Nauplius For M Sc B Sc Zoology Students Youtube



1




Salinity Tolerance Of Cross Breed Shrimp Families Morphological And Biochemical Approaches Asuvapongpatana 13 Aquaculture Research Wiley Online Library




Crustaceans Octavio Acirc Euro Trade S Book Crustaceans Crustaceans Are Invertebrates No Backbones Ppt Powerpoint
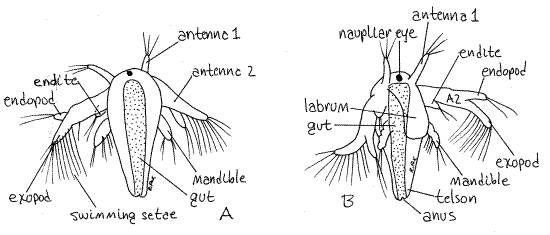



User Alka Yadav Assigment On Crustacean Larva Wikieducator




Ch 30 Powerpoint Notes




Pdf Patterns Of Larval Development




Anaphylaxis Conundrum A Trojan Horse Phenomenon The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice




Abbreviation Of Larval Development And Extension Of Brood Care As Key Features Of The Evolution Of Freshwater Decapoda Vogt 13 Biological Reviews Wiley Online Library
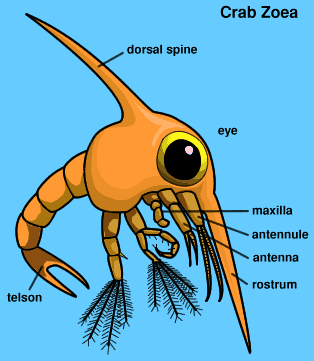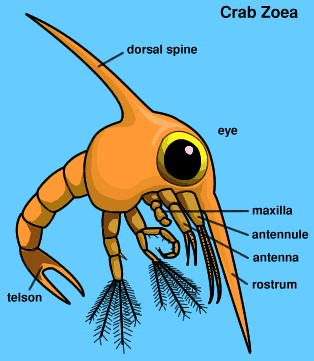



User Alka Yadav Assigment On Crustacean Larva Wikieducator




The Evolution Of Insect Metamorphosis A Developmental And Endocrine View Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B Biological Sciences




Description Of The First Larval Stage Of Pontonia Simplex Decapoda Caridea Palaemonidae From The Eastern Tropical Pacific In Crustaceana Volume 87 Issue 11 12 14




5 A Life Cycle Of Lepeophtheirus Salmonis Early Anamorphic Phase Download Scientific Diagram



2




Larval Developmental Stages Of Penaeus Vannamei Sub Stages Feeding Download Scientific Diagram




Effects Of Salinity And Temperature On Survival And Development Of Larvae And Juveniles Of The Mud Crab Scylla Serrata Crustacea Decapoda Portunidae Baylon 10 Journal Of The World Aquaculture



2
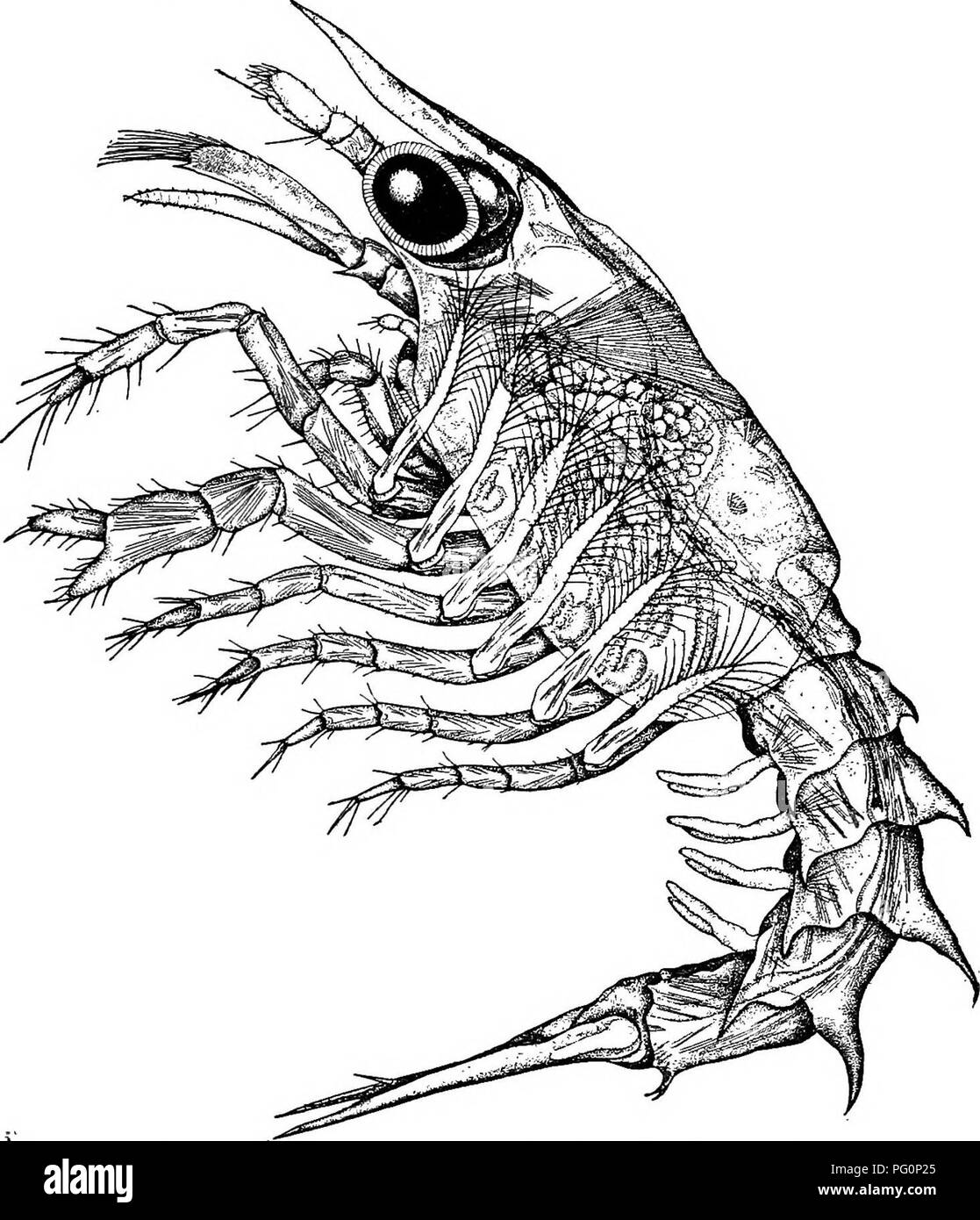



5 Larval Stage High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
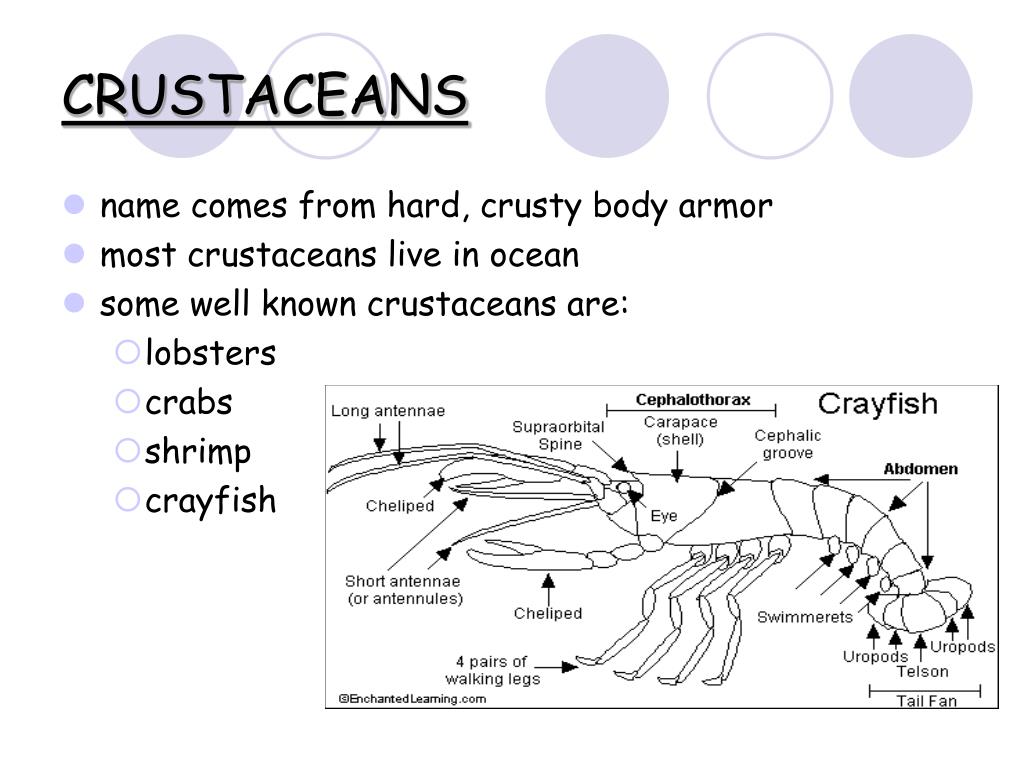



Ppt Crustaceans Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
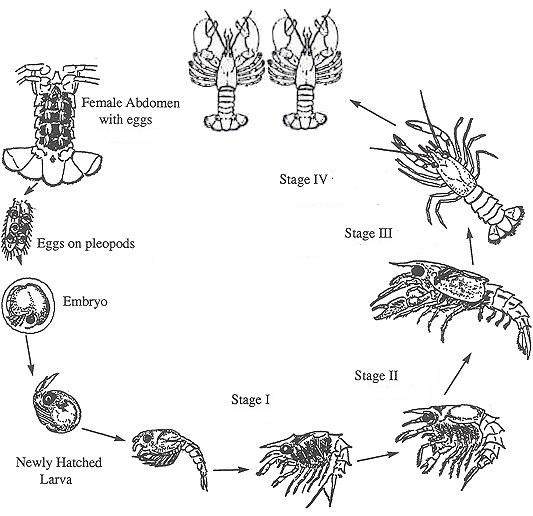



Lobster Farming In India Vikaspedia




Malacostraca Wikipedia




Trust For Nature Prispevky Facebook




Effects Of Salinity And Temperature On Survival And Development Of Larvae And Juveniles Of The Mud Crab Scylla Serrata Crustacea Decapoda Portunidae Baylon 10 Journal Of The World Aquaculture




Larval Forms Of Crustaceans




Arthropod Notes Ppt




Phylum Arthropoda Larval Forms In Crustaceae Study Score




Pdf Salinity Tolerance Ontogeny Of Osmoregulation And Zootechnical Improvement In The Larval Rearing Of The Caledonian Blue Shrimp Litopenaeus Stylirostris Decapoda Penaeidae Dominique Pham Academia Edu



Larval Forms In Crustaceans



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿